SMTP password brute force attacks are a type of network attack where attackers use automated tools to try a large number of username and password combinations in an attempt to access an SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) server. SMTP servers are used for sending and receiving emails, so a successful attack could lead to unauthorized email sending, data leakage, or account abuse.
What are SMTP Password Brute Force Attacks?
- Automated Attacks: Attackers use tools (e.g., Hydra, Brute Force, Ncrack) to automate the process of trying numerous password combinations.
- Repeated Attempts: Attackers continually try different usernames and passwords until they find a valid combination.
- Exploitation of Weak Passwords: Attackers often exploit common or weak passwords, as these are easier to crack.
Detect SMTP Password Brute Force Attacks with Sax2 NIDS
Sax2 IDS is an advanced intrusion detection system designed to monitor and identify abnormal or malicious activities within computer networks and systems. Sax2’s powerful intrusion detection engine can accurately detect FTP brute force attacks and alert them in real time. The following describes the use of Sax2 to detect SMTP password brute force attacks in detail. Click on the URL “https://www.ids-sax2.com/wp-content/download/Sax2_Setup(409).exe” to download Sax2 NIDS, and after downloading, double-click on the installer and the installation prompt will make it easy to install Sax2 NIDS
Step 1. Start the Sax2 NIDS
After installing Sax2 NIDS correctly, you will see the following icon on the desktop, double-click it to start Sax2 NIDS
Step 2. Start Detecting SMTP Password Brute Force Attacks
After starting Sax2, click the “Start” button on the main interface to start the intrusion detection, please see the figure below:
Step 3. View Intrusion Events
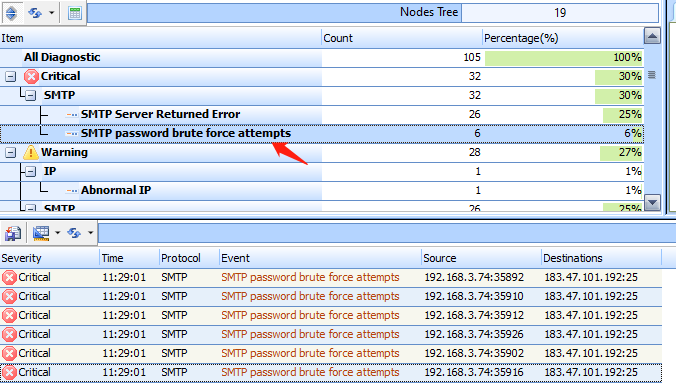
The “Events” viewing window is one of the most important features of Sax2 NIDS and the main place to analyze intrusion events. In order to view the event, first switch to the Events window. Take a look at the following figure, from which you can see that Sax2 has successfully detected the SMTP password brute force attacks.
How to Defend Against SMTP Password Brute Force Attacks
- Use Strong Passwords:
- Ensure SMTP accounts use complex and unique passwords, avoiding common or easily guessable ones.
- Limit Login Attempts:
- Configure SMTP server settings to limit the number of login attempts for accounts. For example, lock accounts or require CAPTCHA after a series of failed attempts.
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
- Implement multi-factor authentication for SMTP accounts, adding an additional verification step to enhance security.
- IP and Geographic Restrictions:
- Restrict access to the SMTP server to a range of IP addresses. For IP addresses outside the organization, use whitelisting or access restrictions.
- Use Secure Connections:
- Use secure SMTP connections (such as SMTP over TLS/SSL) to ensure data is encrypted during transmission, reducing the risk of interception or tampering.
- Regular Updates and Patching:
- Regularly update SMTP server software and related systems to patch known vulnerabilities and ensure system security.
- Log Auditing and Analysis:
- Regularly audit and analyze SMTP server activity logs to identify potential attack patterns and take appropriate measures.
- Deploy Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS):
- Use intrusion detection systems to detect and block abnormal login attempts and other suspicious activities.
Conclusion
By employing a combination of these detection and defense measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of SMTP password brute force attacks and protect the email server and associated accounts.


